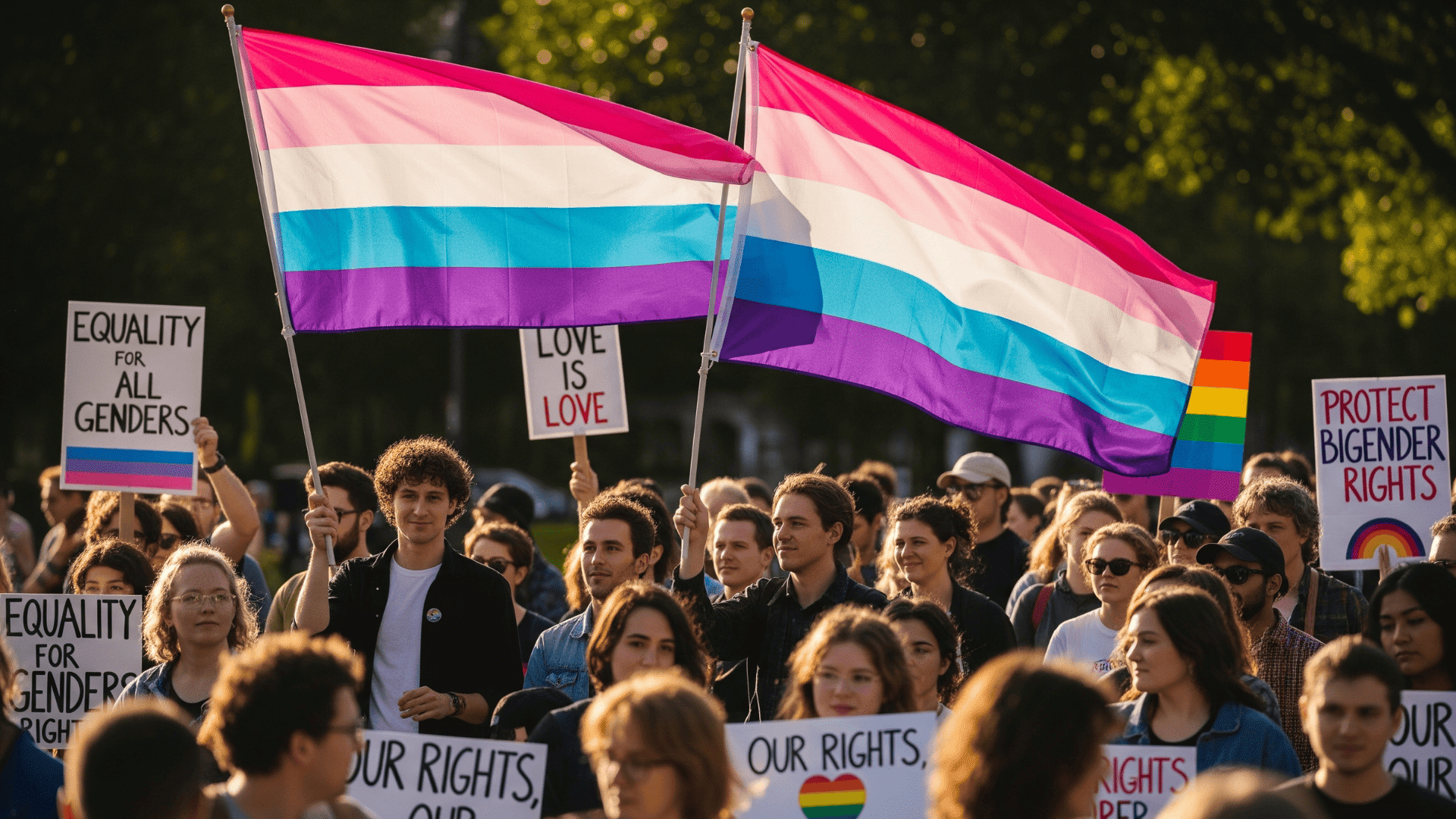
Bigender individuals, who experience two distinct gender identities either simultaneously or fluidly shifting between them, are an important part of the transgender and gender-diverse community.
Understanding their legal rights is essential for ensuring they receive fair treatment, dignity, and safety under the law.
However, as of 2025, protections for bigender people in the United States remain uneven and complex, with advancements in some areas and setbacks in others.
For those seeking support, resources like Online Communities for Bigender Support can provide connection and community during these challenging times.
Bigender Identity and the Need for Legal Protection
Legal protections are essential for bigender individuals, but so is social acceptance. Many people do not fully understand what it means to be bigender, which can lead to stigma and exclusion.
Community visibility and support help break down these barriers. The bigender flag, for example, is a powerful symbol that raises awareness and fosters pride.
When society understands bigender identities better, it puts pressure on lawmakers to create fair and inclusive laws.
Recognizing bigender people’s identity both socially and legally is key to ensuring their safety and dignity.
Federal Protections: A Mixed Picture
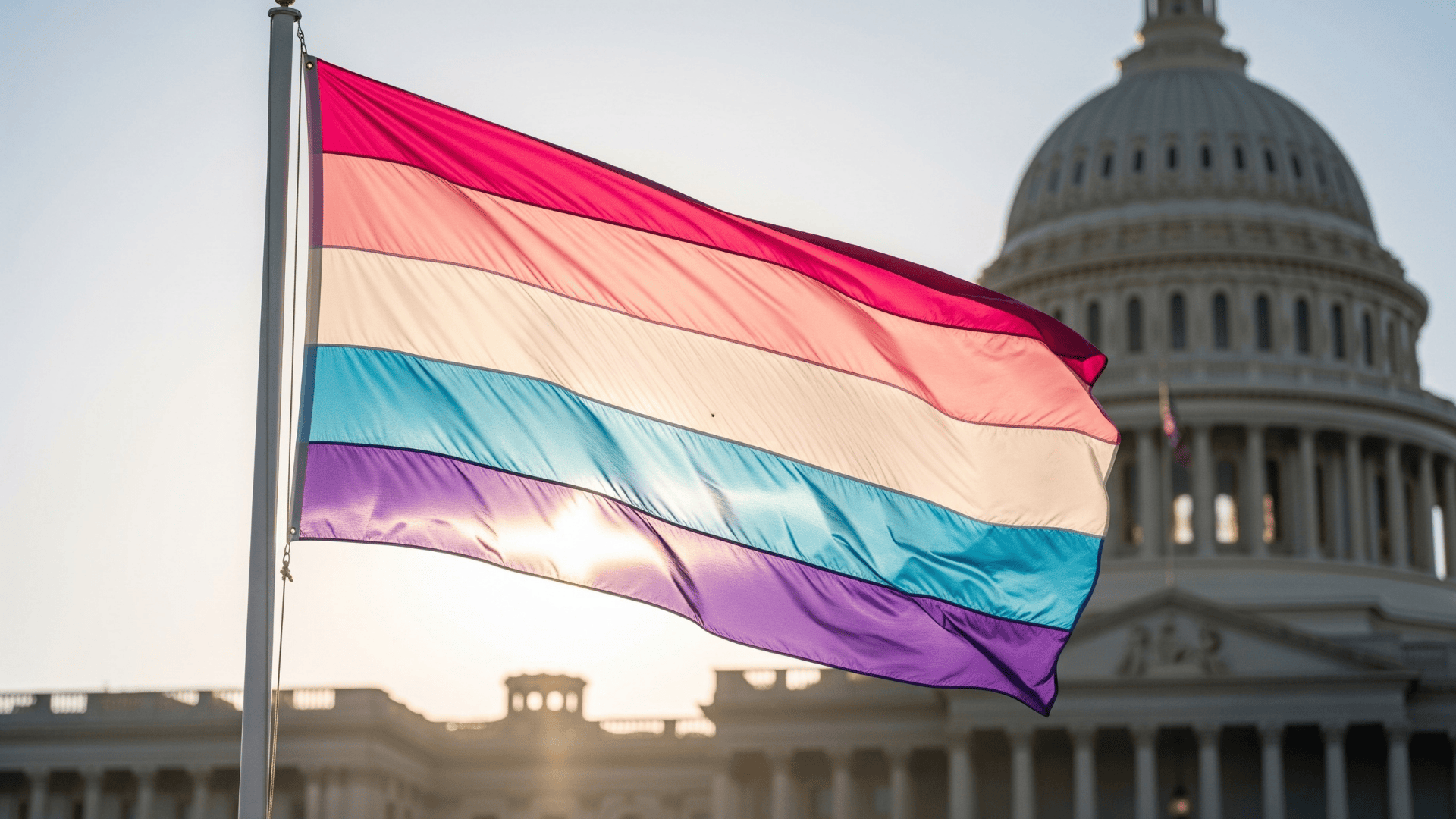
Federal law offers some significant protections for gender-diverse individuals, including bigender people.
Employment discrimination protections for gender identity were extended by the 2020 Bostock v. Clayton County Supreme Court ruling.
Recent executive orders have limited recognition of gender identity, defining sex strictly as biological and binary.
Access to federal documentation and healthcare benefits, including gender-affirming care under Medicare/Medicaid, has been reduced by these changes.
Additionally, federal documentation procedures restricting gender marker changes further complicate recognition and rights for bigender individuals.
State-Level Variability and Restrictions
States vary widely in their legal protections for bigender individuals. Some offer explicit discrimination protections, while many others impose restrictive laws.
Examples of State-Level Laws
| Protective States | Restrictive States |
|---|---|
| Prohibit discrimination in employment, housing, and public accommodations | Ban or heavily restrict gender-affirming care for youth |
| Allow use of bathrooms matching gender identity | Limit access to bathrooms and locker rooms by birth sex |
| Support the use of inclusive pronouns in schools | Ban gender diversity topics in education |
| Protect against discrimination in healthcare and social services | Restrict access to gender-affirming healthcare and counseling |
Currently, 26+ states restrict gender-affirming care for transgender youth, impacting bigender minors significantly.
Ongoing Legal Challenges and Advocacy
The contested nature of these laws has led to an increasing number of legal challenges.
Courts are currently evaluating whether bans on gender-affirming care and other restrictions violate constitutional rights to equal protection and due process.
Advocacy organizations such as the ACLU, Lambda Legal, and the Human Rights Campaign are at the forefront of these fights.
They provide legal representation, challenge discriminatory laws, and push for inclusive policies at every level of government.
Education and public awareness campaigns remain vital components of this work, helping counter misinformation and promote acceptance for gender-diverse communities, including bigender individuals.
Rights in Healthcare and Social Services
Bigender people face significant obstacles in accessing affirming healthcare.
Many providers and insurance plans do not adequately cover or offer gender-affirming treatments such as hormone therapy, counseling, or surgeries.
Federal funding restrictions and state bans compound these access issues, leaving many without affordable or competent care options.
This scarcity contributes to worsening mental and physical health disparities in the community.
Social services, including shelters, counseling programs, and housing facilities, frequently lack explicit policies protecting bigender identities.
Discrimination and exclusion can occur, highlighting the need for stronger protections and inclusive practices in social care settings.
Workplace and Educational Protections
Federal law forbids discrimination based on gender identity in employment, but enforcement and awareness can be inconsistent.
Many workplaces fall short in providing training about gender diversity or implementing inclusive policies, leaving bigender employees vulnerable to harassment or exclusion.
In educational settings, protections vary drastically. Some schools allow students to use preferred names and pronouns freely and access restrooms and locker rooms matching their gender identity.
However, other schools impose restrictive policies that undermine gender affirmation, causing distress and higher rates of bullying among gender-diverse youth.
The uneven nature of these protections results in vastly different experiences for bigender individuals depending on location.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead
While 2025 has brought some legal progress affirming bigender individuals’ rights, it has also introduced setbacks, especially through restrictive laws at the state level and federal policy rollbacks.
Bigender people’s lived realities remain highly dependent on where they reside, affecting their access to healthcare, education, employment protections, and social acceptance.
Legal advocacy, education, and policy reform are crucial to creating a more consistent, affirming legal environment for bigender and all transgender individuals.
Together, through knowledge, advocacy, and empathy, we can build a society that honors and protects diverse gender identities.
What legal protections do you think are most important for bigender individuals? Share your thoughts in the comments below and join the conversation about creating a more inclusive legal system.




















