Imagine if your home could generate its own electricity simply by sitting in the sun, just like a plant soaking up sunlight to grow.
That’s exactly what solar panels do for your house! With the rising cost of energy and the growing need for cleaner power, more families are turning to solar energy to power their daily lives.
If you’ve ever asked yourself, How do solar panels work on a house?, you’re not alone. It’s one of the most common questions people have before deciding to switch to solar power.
The good news? It’s not as complicated as it sounds. Let’s break it down in a simple, step-by-step way so you can understand how sunlight gets turned into electricity for your home.
What are Solar Panels?
At their core, solar panels are devices that capture sunlight and turn it into usable electricity. They’re usually placed on rooftops, yards, or any sunny spot around a home.
When people talk about solar energy homes or solar power for household use, they’re really talking about installing these panels and connecting them to the home’s electrical system.
A solar panel is made up of smaller units called solar cells. These cells are typically made from a material called silicon, which possesses special properties that enable it to generate electricity when exposed to sunlight.
Think of each solar cell as a tiny factory, and the whole panel as a team of factories working together.
How Do Solar Panels Work on a House?
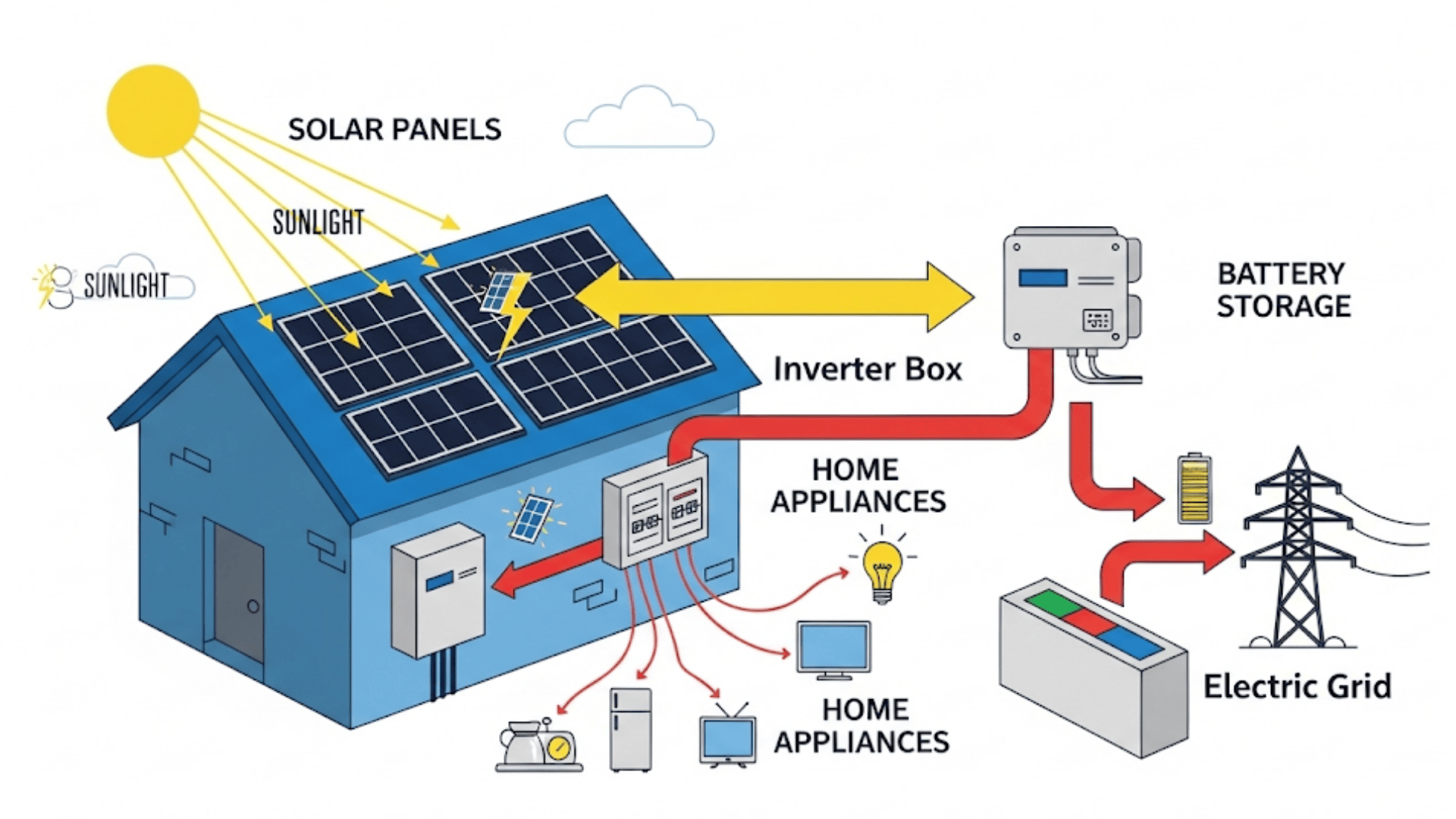
Here’s the simple journey of sunlight as it becomes the power running your fridge, lights, and Wi-Fi router:
1. Sunlight Hits the Solar Panels
When sunlight shines on your solar panels, the tiny solar cells inside begin capturing the sun’s energy.
These cells are designed to absorb light, which is composed of particles called photons. This is the very first step in producing clean electricity for your home.
2. The Solar Cells Make Electricity
Inside each solar cell, photons bump into electrons in the silicon layer, causing them to move. That movement creates an electric current.
At this stage, the electricity is direct current (DC), which is not yet usable by most household devices and appliances.
3. The Inverter Changes DC to AC
Since most homes operate on alternating current (AC), the inverter is one of the most crucial components of a solar system.
It takes the DC electricity produced by your panels and converts it into AC power, ready for your everyday household use.
4. Power for the House
Once the inverter has done its job, the electricity flows into your home’s electrical panel, also called the breaker box.
From there, it is distributed to everything that needs power, your refrigerator, television, air conditioner, lights, and other household electronics.
5. Extra Power Goes to the Grid or Battery
If your panels produce more energy than your home requires, the excess electricity doesn’t go to waste.
It can be stored in a solar battery for later use, or sent back into the electric grid, often earning bill credits through net metering.
The Importance of Sun Exposure for Solar Panels

When it comes to maximizing the benefits of your solar panels, sun exposure is crucial.
The more direct sunlight your panels receive, the more electricity they can produce. That’s why placement and location matter so much.
- Roof Direction: South-facing roofs (in the Northern Hemisphere) generally capture the most sunlight throughout the day.
- Roof Angle: A tilt that matches your latitude usually gives the best year-round results.
- Shading: Trees, chimneys, or tall buildings that block sunlight can reduce efficiency, so clear access to the sun is key.
- Local Climate: Even in cloudy areas, solar panels work—but homes in sunnier regions will naturally see greater energy production.
More sun equals more savings. A professional solar installer can assess your roof and recommend the best setup for maximum exposure.
Why Choose Solar Energy for Homes?
Now that we’ve answered how solar panels work on a house, let’s talk about why so many families are choosing them.
-
Save Money on Bills: Imagine reducing or even eliminating your monthly electricity bill. With solar, you can do that. While the upfront cost can be substantial, the savings accumulate over time.
-
Clean and Green: Solar energy doesn’t pollute the air or water. It’s one of the cleanest ways to make power, which means fewer harmful gases are released into the environment.
-
Energy Independence: Instead of relying completely on utility companies, you make your own power. That feels empowering (literally!).
-
Adds Home Value: Homes with solar systems are often valued higher because buyers love the idea of saving money on energy.
The idea of using solar power for household purposes is growing rapidly for good reasons.
Different Types of Solar Power for Household Use
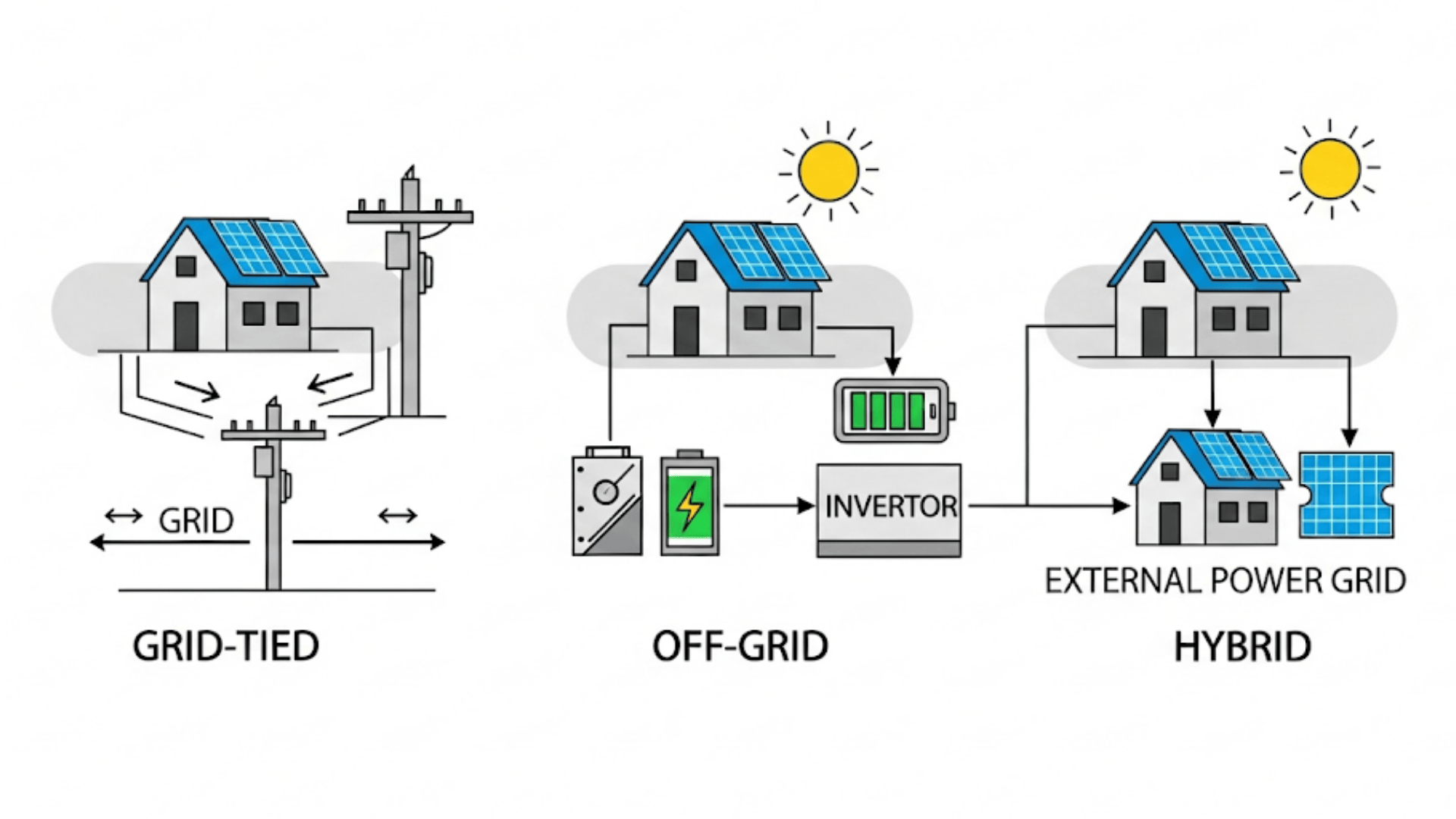
Solar systems come in different setups. Your choice depends on budget, space, and energy needs. Here are the main types:
1. Grid-Tied Systems
This common setup links your home to both solar panels and the main electric grid.
You use solar power first, then rely on the grid when needed. Extra electricity your panels produce is sent back, often earning credits through net metering.
2. Off-Grid Systems
Off-grid systems are fully independent and rely only on solar panels plus batteries.
They’re ideal for cabins or remote homes without access to a grid. Since they store all power, they require larger battery banks but offer total self-sufficiency and energy independence.
3. Hybrid Systems
Hybrid systems connect to the grid but also include battery storage.
This provides flexibility to use solar power during the day, store excess energy for nighttime or outages, and rely on the grid when necessary. They’re perfect for areas prone to frequent blackouts.
What Do You Need for a Solar Energy Home?
Starting a solar journey is easier when you know the key parts of the system. Here’s what every setup needs:
- Solar Panels – The main component that captures sunlight and turns it into usable electricity for your home.
- Inverter – Converts the panels’ direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), which your household appliances can use.
- Mounting System – Secures the panels safely on your roof or ground for maximum sunlight exposure and stability.
- Battery (Optional) – Stores extra electricity for use at night, during cloudy days, or power outages.
- Net Meter – Monitors energy flow, tracking what you use and what you send back to the electric grid.
With these essential components, your home can harness the sun’s energy, reducing costs and bringing clean power into everyday life.
Final Thoughts
Solar power isn’t just a passing trend; it’s shaping the future of how we power our lives.
As technology advances, solar panels are becoming increasingly efficient and affordable, while modern batteries enable the storage of excess energy for nighttime use or emergencies.
This means homes and even entire neighborhoods can run on clean, renewable energy.
Choosing solar today means saving money, protecting the planet, and gaining energy independence.
Ready to make the switch? Research solar options for your home and see how much you can save while building a cleaner, brighter tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do Solar Panels Work on Cloudy Days?
Yes, but not as well as in full sunshine. They can still capture scattered sunlight and produce power, just at a lower level.
Do They Work at Night?
No. Since there’s no sunlight, panels don’t produce power at night. That’s where the grid or a solar battery comes in.
How Long Do Solar Panels Last?
Most panels last 25 to 30 years, and many come with warranties that guarantee performance for decades to come.



















